多线程CountDownLatch与线程池ThreadPoolExecutor/ExecutorService怎么在java中使用
导读:本文共4845.5字符,通常情况下阅读需要16分钟。同时您也可以点击右侧朗读,来听本文内容。按键盘←(左) →(右) 方向键可以翻页。
摘要: 1、CountDownLatch:一个同步工具类,它允许一个或多个线程一直等待,直到其他线程的操作执行完后再执行。2、ThreadPoolExecutor/ExecutorService:线程池,使用线程池可以复用线程,降低频繁创建线程造成的性能消耗,同时对线程的创建、启动、停止、销毁等操作更简便。3、使用场景举例:年末公司组织团建,要求每一位员工周六上午8点到... ...
目录
(为您整理了一些要点),点击可以直达。1、CountDownLatch:
一个同步工具类,它允许一个或多个线程一直等待,直到其他线程的操作执行完后再执行。
2、ThreadPoolExecutor/ExecutorService:
线程池,使用线程池可以复用线程,降低频繁创建线程造成的性能消耗,同时对线程的创建、启动、停止、销毁等操作更简便。
3、使用场景举例:
年末公司组织团建,要求每一位员工周六上午8点到公司门口集合,统一乘坐公司所租大巴前往目的地。
在这个案例中,公司作为主线程,员工作为子线程。
4、代码示例:
packagecom.test.thread;importjava.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;importjava.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;importjava.util.concurrent.Executors;importjava.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;importjava.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;importjava.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/***@authorjavaloveiphone*@date创建时间:2023年1月25日上午10:59:11*@Description:*/publicclassCompany{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsInterruptedException{//员工数量intcount=5;//创建计数器//构造参数传入的数量值代表的是latch.countDown()调用的次数CountDownLatchlatch=newCountDownLatch(count);//创建线程池,可以通过以下方式创建//ThreadPoolExecutorthreadPool=newThreadPoolExecutor(1,1,60,TimeUnit.SECONDS,newLinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(count));ExecutorServicethreadPool=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(count);System.out.println("公司发送通知,每一位员工在周六早上8点到公司大门口集合");for(inti=0;i<count;i++){//将子线程添加进线程池执行Thread.sleep(10);threadPool.execute(newEmployee(latch,i+1));}try{//阻塞当前线程,直到所有员工到达公司大门口之后才执行latch.await();//使当前线程在锁存器倒计数至零之前一直等待,除非线程被中断或超出了指定的等待时间。//latch.await(longtimeout,TimeUnitunit)System.out.println("所有员工已经到达公司大门口,大巴车发动,前往活动目的地。");}catch(InterruptedExceptione){e.printStackTrace();}finally{//最后关闭线程池,但执行以前提交的任务,不接受新任务threadPool.shutdown();//关闭线程池,停止所有正在执行的活动任务,暂停处理正在等待的任务,并返回等待执行的任务列表。//threadPool.shutdownNow();}}}//分布式工作线程classEmployeeimplementsRunnable{privateCountDownLatchlatch;privateintemployeeIndex;publicEmployee(CountDownLatchlatch,intemployeeIndex){this.latch=latch;this.employeeIndex=employeeIndex;}@Overridepublicvoidrun(){try{System.out.println("员工:"+employeeIndex+",正在前往公司大门口集合...");Thread.sleep(10);System.out.println("员工:"+employeeIndex+",已到达。");}catch(Exceptione){e.printStackTrace();}finally{//当前计算工作已结束,计数器减一latch.countDown();try{Thread.sleep(10);}catch(InterruptedExceptione){e.printStackTrace();}//执行coutDown()之后,继续执行自己的工作,不受主线程的影响System.out.println("员工:"+employeeIndex+",吃饭、喝水、拍照。");}}}打印输出结果如下:
公司发送通知,每一位员工在周六早上8点到公司大门口集合员工:1,正在前往公司大门口集合...员工:1,已到达。员工:2,正在前往公司大门口集合...员工:2,已到达。员工:1,吃饭、喝水、拍照。员工:3,正在前往公司大门口集合...员工:2,吃饭、喝水、拍照。员工:3,已到达。员工:4,正在前往公司大门口集合...员工:3,吃饭、喝水、拍照。员工:4,已到达。员工:5,正在前往公司大门口集合...员工:4,吃饭、喝水、拍照。员工:5,已到达。所有员工已经到达公司大门口,大巴车发动,前往活动目的地。员工:5,吃饭、喝水、拍照。
注意:
每一个员工到达之后,执行countDown()方法,直到所有员工到达之后,计数器为0,主线程才会继续执行。
但子线程执行了countDown()方法,之后会继续自己的工作,比如上面的【吃饭、喝水、拍照】,是不受主线程是否阻塞、其它线程是否已经执行countDown()方法的影响的。
5、CountDownLatch与CyclicBarrier的对比可以看:
java多线程CyclicBarrier使用示例,让线程起步走
补充:CountDownLatch踩过的坑
线上生产环境dubbo报线程池满了,经过一天排查锁定在开三个线程计算最后合并数据的步骤中。简单描述下该步骤线程开三个 调用三个不同的方法 使用countdownlatch 计数器等待三个方法全部执行完成 合并数据。
但是由于其中一个方法调用第三方接口,接口返回异常导致转换数据报错。导致其中一个方法未正常完成。
举例demo:
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){ExecutorServiceexecutorService=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);CountDownLatchcdl=newCountDownLatch(3);executorService.execute(newRunnable(){@Overridepublicvoidrun(){/*try{function1();}catch(Exceptione){//异常处理e.printStackTrace();}finally{cdl.countDown();}*/function1();}});executorService.execute(newRunnable(){@Overridepublicvoidrun(){function2();cdl.countDown();}});executorService.execute(newRunnable(){@Overridepublicvoidrun(){function3();cdl.countDown();}});try{cdl.await();//cdl.await(20,TimeUnit.SECONDS);System.out.println("三个执行线程结束");}catch(InterruptedExceptione){e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("执行线程异常");}finally{executorService.shutdown();System.out.println("执行线程关闭");}}privatestaticvoidfunction1(){inti=10/0;System.out.println("方法一");}privatestaticvoidfunction2(){System.out.println("方法二");}privatestaticvoidfunction3(){System.out.println("方法三");}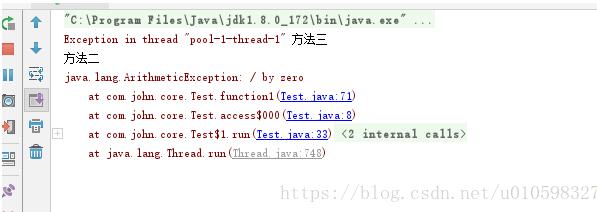
方法一抛出异常,但是没有做异常处理导致不会执行线程关闭步骤,是不是和想象中不一样,一开始我也是懵,看了一下CountDownLatch原理就很好理解了,
“CountDownLatch是通过一个计数器来实现的,计数器的初始化值为线程的数量。每当一个线程完成了自己的任务后,计数器的值就相应得减1。当计数器到达0时,表示所有的线程都已完成任务,然后在闭锁上等待的线程就可以恢复执行任务。”【1】
举一个现实中例子就是:CountDownLatch 就像跑步比赛中的裁判,三个方法就是就是三位运动员,运动员2,3都已经到达终点,但是运动员1摔倒了,动不了。裁判员只看到两位运动员到达终点不能宣布比赛结束,所以一直等。。。
就像这样的场景导致线上service执行线程阻塞,接口调用次数累计导致dubbo线程满了(跟dubbo线程模型有关,有时间具体谈谈这一点)
知道原因了,就要考虑怎么修改
比赛不能无限期等,所以比赛必须在有限时间内结束,所以使用
publicbooleanawait(longtimeout,TimeUnitunit)throwsInterruptedException{returnsync.tryAcquireSharedNanos(1,unit.toNanos(timeout));}线程内部也许要增加异常处理
executorService.execute(newRunnable(){@Overridepublicvoidrun(){try{function1();}catch(Exceptione){//异常处理e.printStackTrace();}finally{cdl.countDown();}//function1();}});修改后demo
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){ExecutorServiceexecutorService=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);CountDownLatchcdl=newCountDownLatch(3);executorService.execute(newRunnable(){@Overridepublicvoidrun(){try{function1();}catch(Exceptione){//异常处理e.printStackTrace();}finally{cdl.countDown();}//function1();}});executorService.execute(newRunnable(){@Overridepublicvoidrun(){function2();cdl.countDown();}});executorService.execute(newRunnable(){@Overridepublicvoidrun(){function3();cdl.countDown();}});try{//cdl.await();cdl.await(20,TimeUnit.SECONDS);System.out.println("三个执行线程结束");}catch(InterruptedExceptione){e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("执行线程异常");}finally{executorService.shutdown();System.out.println("执行线程关闭");}}privatestaticvoidfunction1(){inti=10/0;System.out.println("方法一");}privatestaticvoidfunction2(){System.out.println("方法二");}privatestaticvoidfunction3(){System.out.println("方法三");}执行结果
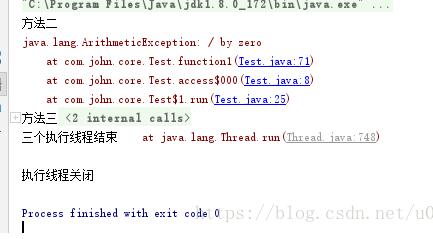
</div> <div class="zixun-tj-product adv-bottom"></div> </div> </div> <div class="prve-next-news">多线程CountDownLatch与线程池ThreadPoolExecutor/ExecutorService怎么在java中使用的详细内容,希望对您有所帮助,信息来源于网络。