Java的Lambda表达式实例分析
导读:本文共3117.5字符,通常情况下阅读需要10分钟。同时您也可以点击右侧朗读,来听本文内容。按键盘←(左) →(右) 方向键可以翻页。
摘要: 1、简介首先Lambda表达式是属于Java8的 一个新特性,提供Java编程中对于函数式编程的支持,有助于代码的简洁,可以取代大半部分的匿名函数,尤其对于集合的遍历和集合的操作,极大的简化了代码。Lambda表达式的主体:函数式接口:注意: Lambda表达式一定要配合函数式接口一起使用,所谓函数式接口,就是接口中只有一个抽象方法的接口就是函数式接口,我们可以... ...
目录
(为您整理了一些要点),点击可以直达。1、简介
首先Lambda表达式是属于Java8的 一个新特性,提供Java编程中对于函数式编程的支持,有助于代码的简洁,可以取代大半部分的匿名函数,尤其对于集合的遍历和集合的操作,极大的简化了代码。
Lambda表达式的主体:
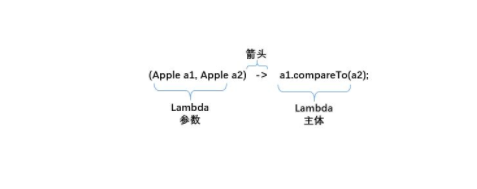
函数式接口:
注意: Lambda表达式一定要配合函数式接口一起使用,所谓函数式接口,就是接口中只有一个抽象方法的接口就是函数式接口,我们可以自定义,JDK也内置了大量的函数式接口。
1、@FunctionalInterface注解修饰了接口,那这个接口就是函数式接口,只能有一个方法,下面就是一个函数式接口:
@FunctionalInterfacepublicinterfaceMyInteface{voideat();}2、 如果不加@FunctionalInterface**注解,你在接口里面只写一个抽象方法也可以认为是函数式接口:
publicinterfaceMyInteface{voideat();}这样也是可以的。
3、 函数式接口只有一种情况不只有抽象方法,那就是可以继承Object类的方法:
@FunctionalInterfacepublicinterfaceMyInteface3{voideat();@OverrideStringtoString();@OverrideinthashCode();}2、Lambda表达式的使用:
1、在普通方法内的使用
Student类:
@FunctionalInterfacepublicinterfaceStudent{voideat();}测试类:
publicclassTest{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){Studentstu=newStudent(){//普通方法,重写并使用@Overridepublicvoideat(){System.out.println("我是学生");}};stu.eat();//lambda表达式写法://参数1:重写了Student接口中唯一的那个无参数的eat抽象方法做了具体的实现,所以重写不需要署名//参数2:->表达式固定的//参数3:{具体的实现}对Student接口中唯一的eat方法做了具体的实现Studentstu2=()->{System.out.println("学生吃饭");};stu2.eat();}}输出:
我是学生
学生吃饭
2、带参方法的使用
Student类:
@FunctionalInterfacepublicinterfaceStudent{voideat(Stringfood);}测试类:
publicclassTest{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){//lambda重写Student接口唯一的有参方法:Studentstu2=(foodName)->{System.out.println("学生在吃"+foodName);};stu2.eat("肉");}}//输出:学生在吃肉
3、Lambda表达式实现多线程
之前在多线程(1)的那篇文章内有介绍了创建多线程的方法,这里就使用lambda来创建线程:
publicclassTest{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){Threadt=newThread(()->{System.out.println("这个线程是由lambda来创建的");});t.start();}}4、Lambda表达式操作运算
我们使用lambda来操作运算可以少很多代码:
函数式接口:
@FunctionalInterfacepublicinterfaceCalculator<T>{Toperation(Tv1,Tv2);}测试类:
publicclassTest{//计算方法publicstaticIntegeroperator(Integerv1,Integerv2,Calculator<Integer>calculator){returncalculator.operation(v1,v2);}publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){//使用lambda表达式://这里的意思就是传入两个参数,返回运行后的值intadd=Test.operator(5,10,(x,y)->{returnx+y;});//简写:可以少写很多代码,比上面更简介了intnum1=Test.operator(5,10,(x,y)->x+y);intnum2=Test.operator(10,5,(x,y)->x-y);System.out.println(add);System.out.println(num1);System.out.println(num2);}}输出:
15 、15 、5
5、Lambda表达式方法引用
有时候我们不是必须要要重写接口的方法来做具体的实现,我们如果有存在的方法能来实现,也可以通过方法 引用的方式来引用已经存在的方法做接口中方法具体的实现,这样的好处就是代码复用,比如下面这样:
函数式接口:
publicinterfaceResultOneParam{intmethod(inta);}测试类:
publicclassTest{publicintaddTo(inta){returna+10;}publicstaticintaddTo2(inta){returna+10;}publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){//lambda重写了method方法ResultOneParamlambda1=(a)->a+10;//方法引用:就是在Test里面的addTo2方法用来替代method被重写的方法ResultOneParamlambda2=Test::addTo2;intresult1=lambda2.method(9);System.out.println(result1);//方法引用::引用现成的方法来替代方法重写,这样可以方法重用Testtest=newTest();ResultOneParamlambda3=test::addTo;intresult2=lambda3.method(9);System.out.println(result1);}}6、Lambda表达式对集合的使用
当然Lambda对集合的操作也是很方便的,可以少些很多代码:
publicclassTest{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){List<Integer>list=Arrays.asList(5,1,3,4,5,0,9,7,0,1,5);//lambda表达式遍历集合,重写了Consumer接口的方法list.forEach((element)->{System.out.println(element);});//简写:list.forEach(element->System.out.println(element));//lambda表达式方法引用,用于遍历输出list集合:list.forEach(System.out::print);//输出list的偶数:list.forEach(element->{if(element%2==0){System.out.println(element);}});}} </div> <div class="zixun-tj-product adv-bottom"></div> </div> </div> <div class="prve-next-news">Java的Lambda表达式实例分析的详细内容,希望对您有所帮助,信息来源于网络。