Vue中的计算属性与监听属性怎么用
导读:本文共9617.5字符,通常情况下阅读需要32分钟。同时您也可以点击右侧朗读,来听本文内容。按键盘←(左) →(右) 方向键可以翻页。
摘要: 一、为什么要使用计算属性什么是计算属性计算属性:可以理解为能够在里面写一些计算逻辑的属性。具有如下的作用:减少模板中的计算逻辑。数据缓存。当我们的数据没有变化的时候,不会再次执行计算的过程。依赖固定的数据类型(响应式数据),不能是普通的传入的一个全局数据。在数据量比较大的时候,计算属性可以帮助我们提高性能,因为计算属性只会在数据变化的时候才会计算。在讲解计算属性... ...
目录
(为您整理了一些要点),点击可以直达。一、为什么要使用计算属性
什么是计算属性
计算属性:可以理解为能够在里面写一些计算逻辑的属性。具有如下的作用:
减少模板中的计算逻辑。
数据缓存。当我们的数据没有变化的时候,不会再次执行计算的过程。
依赖固定的数据类型(响应式数据),不能是普通的传入的一个全局数据。
在数据量比较大的时候,计算属性可以帮助我们提高性能,因为计算属性只会在数据变化的时候才会计算。
在讲解计算属性之前先来看下面的一个例子:
需求:外卖套餐A每份15元,客户点了3份,总价打八折,配送费5元,要求在界面显示总价,代码如下:
<template><div><div>您购买了{{info.name}}共{{info.count}}份</div><h2>总价:{{info.count*info.price*info.sale+info.freight}}元</h2></div></template><script>exportdefault{name:'Test',data(){return{info:{userId:1,price:15,name:'套餐A',count:3,sale:0.8,freight:5}}}}</script>界面运行效果:

看了上面的例子,可能有人会问:使用这种方式已经实现了需求,那为什么还要使用计算属性呢?我们知道,vue中模板内的表达式非常便利,设计的初衷是用于简单运算的。如果在模板中放入太多的逻辑会让模板过重而且难以维护,看上面的代码:
<h2>总价:{{info.count*info.price*info.sale+info.freight}}元</h2>在这段代码中,模板不在是简单的声明式逻辑,而是复杂的逻辑计算,如果想要在多处引用总价的时候,就会难以维护。所以,对于任何复杂的逻辑,都应当使用计算属性。
看下面使用计算属性的例子:
<template><div><h2>计算属性</h2><div>您购买了{{info.name}}共{{info.count}}份</div><!--使用计算属性:和绑定普通属性一样--><h2>总价:{{totalPrice}}元</h2></div></template><script>exportdefault{name:'ComputedDemo',data(){return{info:{userId:1,price:15,name:'套餐A',count:3,sale:0.8,freight:5}}},computed:{//定义计算属性totalPricetotalPrice:function(){returnthis.info.count*this.info.price*this.info.sale+this.info.freight}}}</script>界面显示效果:
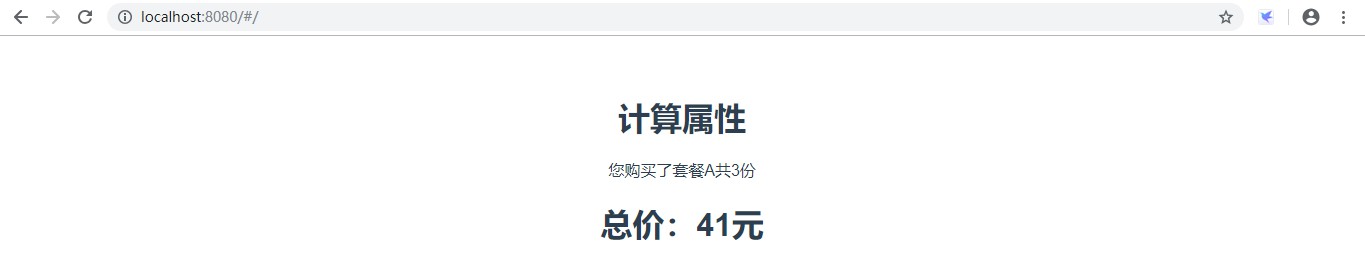
注意:计算属性是一个属性,不是方法,不能写在methods中,放在computed属性里面。
上面计算属性的写法也可以使用ES6的写法:
//使用ES6写法totalPrice(){returnthis.info.count*this.info.price*this.info.sale+this.info.freight}二、计算属性和方法的区别
1、区别
上面的例子除了使用计算属性,还可以使用方法实现:
<template><div><h2>计算属性</h2><div>您购买了{{info.name}}共{{info.count}}份</div><!--使用计算属性:和绑定普通属性一样--><h2>使用计算属性获取总价:{{totalPrice}}元</h2><h2>使用方法获取总价:{{getTotalPrice()}}元</h2></div></template><script>exportdefault{name:'ComputedDemo',data(){return{info:{userId:1,price:15,name:'套餐A',count:3,sale:0.8,freight:5}}},computed:{//定义计算属性totalPrice//totalPrice:function(){//returnthis.info.count*this.info.price*this.info.sale+this.info.freight;//}//使用ES6写法totalPrice(){returnthis.info.count*this.info.price*this.info.sale+this.info.freight;}},methods:{getTotalPrice(){returnthis.info.count*this.info.price*this.info.sale+this.info.freight;}}}</script>界面显示效果:
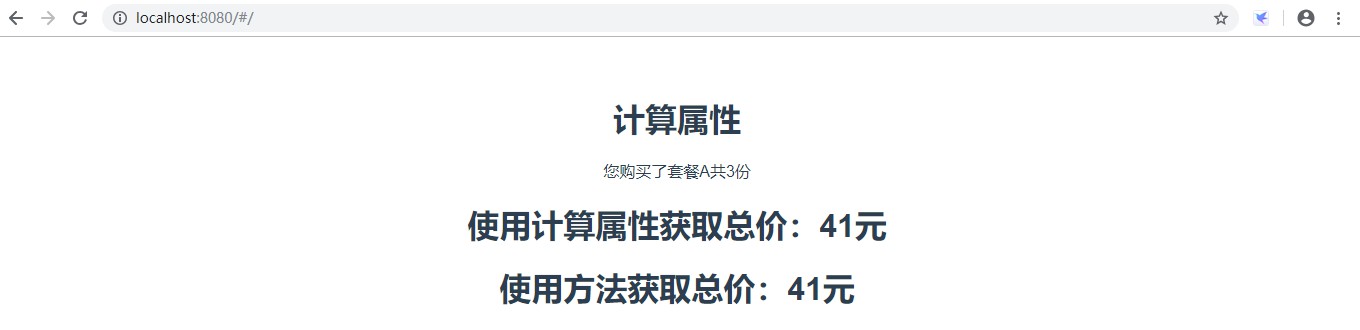
通过上面的例子可以看出:计算属性和方法实现的最终效果是相同的。那么计算属性和方法有什么区别呢?计算属性是基于它们的响应式依赖进行缓存的,只有在响应式依赖发生改变时才会重新求值。这就意味着只要响应式依赖没有发生改变,多次访问计算属性会立即返回之前的计算结果,而不必再次执行计算。相比之下,调用方法总会再次执行函数。总价计算属性和方法的区别如下:
计算属性在依赖发生改变时会自动改变,而方法在依赖发生改变时需要触发才会改变。
计算属性在依赖发生改变时才会重新计算,而方法在每次调用时都会执行。
看下面的例子:
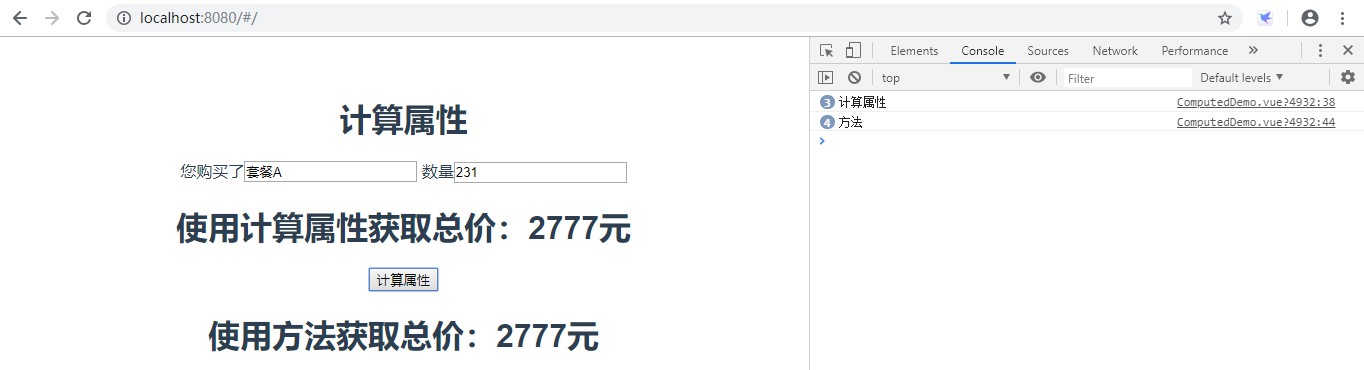
<template><div><h2>计算属性</h2><!--<div>您购买了{{info.name}}共{{info.count}}份</div>--><!--使用计算属性:和绑定普通属性一样-->您购买了<inputtype="text"v-model="info.name"/>数量<inputtype="text"v-model="info.count"/><h2>使用计算属性获取总价:{{totalPrice}}元</h2><button@click="getTotalPrice">计算属性</button><h2>使用方法获取总价:{{data}}元</h2></div></template><script>exportdefault{name:'ComputedDemo',data(){return{info:{userId:1,price:15,name:'套餐A',count:3,sale:0.8,freight:5},data:0}},computed:{//定义计算属性totalPrice//totalPrice:function(){//returnthis.info.count*this.info.price*this.info.sale+this.info.freight;//}//使用ES6写法totalPrice(){console.log('计算属性');returnthis.info.count*this.info.price*this.info.sale+this.info.freight;}},methods:{getTotalPrice(){console.log('方法');this.data=this.info.count*this.info.price*this.info.sale+this.info.freight;}}}</script>当依赖发生改变时会多次打印“计算属性”,而方法需要在点击按钮的时候才会发生改变。依赖不发生改变时点击按钮,也会打印“方法”。如下图所示:
2、计算属性使用场景
假如我们有一个性能开销比较大的计算属性A,它需要遍历一个巨大的数组并做大量的计算,然后我们可能有其他的计算属性依赖于计算属性A。如果不使用计算属性,那么将不可避免的多次进行计算,会消耗很大的性能,这种情况下就需要使用计算属性。
三、修改计算属性的值
在上面的例子中都是使用的获取后的计算属性的值,那么如何修改计算属性的值呢?看下面的例子:
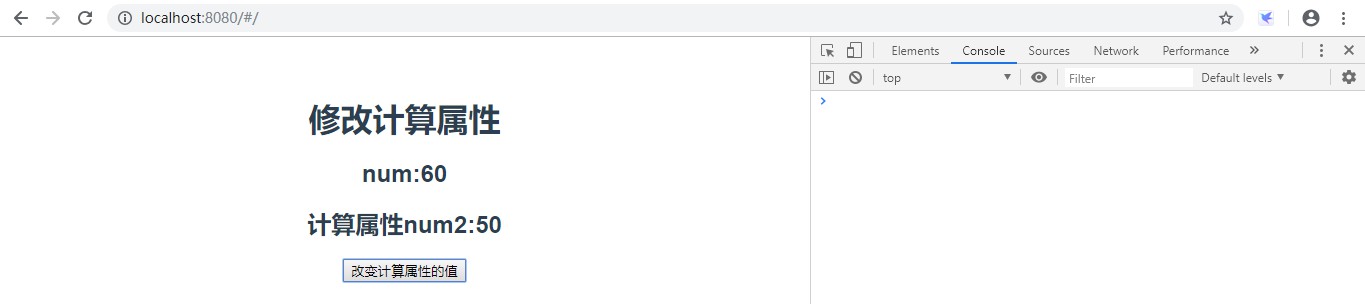
<template><div><h2>修改计算属性</h2><h3>num:{{num}}</h3><h3>计算属性num2:{{num2}}</h3><button@click="change">改变计算属性的值</button></div></template><script>exportdefault{name:'ComputedDemo2',data(){return{num:100}},computed:{num2(){returnthis.num-10;}},methods:{change(){this.num2=60;}}}</script>效果:
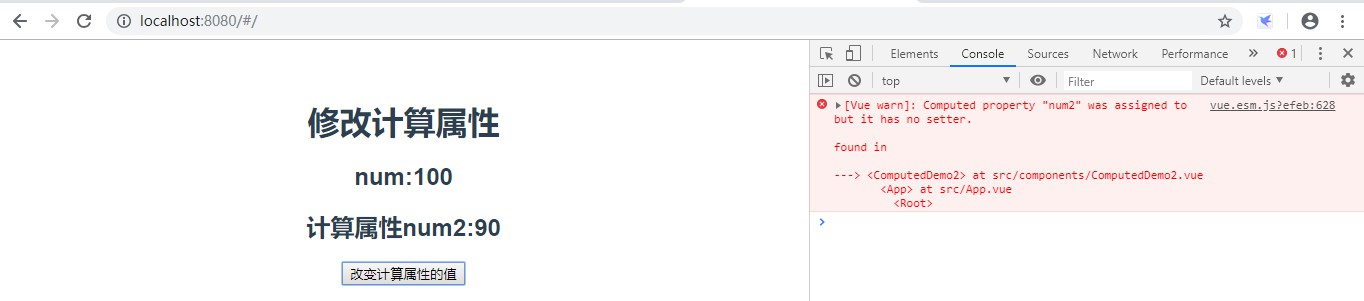
这时会发现直接修改计算属性的值报错了,因为不能直接修改计算属性的值,如果要修改计算属性的值,需要修改其依赖项的值,看下面的代码:
<template><div><h2>修改计算属性</h2><h3>num:{{num}}</h3><h3>计算属性num2:{{num2}}</h3><button@click="change">改变计算属性的值</button></div></template><script>import{get}from'http';exportdefault{name:'ComputedDemo2',data(){return{num:100}},computed:{num2:{//当计算属性要修改时先触发set方法//读取当前计算属性中的值,get方法可以隐藏,默认进入的是get方法get:function(){returnthis.num-10;},set:function(val){this.num=val;}}},methods:{change(){//计算属性不能直接修改this.num2=60;}}}</script>修改前的效果:

修改后的效果:
总结
计算属性的值不能修改,如果要修改计算属性的值,要通过计算属性里面的set方法修改其依赖项的值才能修改计算属性的值。
四、监听属性
监听属性(watch)是用来监听data中的数据是否发生变化,一般是监听data中的某个属性。
更加灵活、通用的API。
watch中可以执行任何逻辑,如函数节流,Ajax异步获取数据,甚至操作DOM。
1、监听普通属性
看下面的代码:
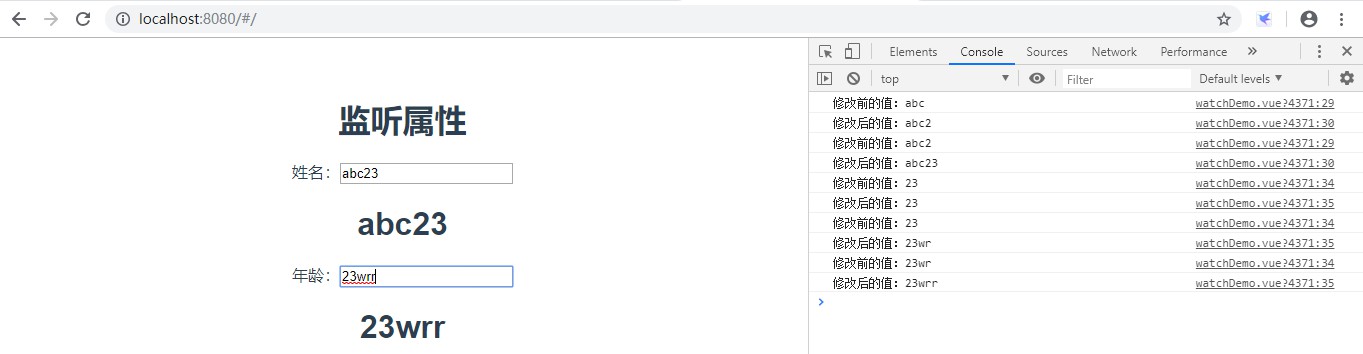
<template><div><h2>监听属性</h2>姓名:<inputtype="text"v-model="userName"/><h2>{{userName}}</h2>年龄:<inputtype="text"v-model="age"/><h2>{{age}}</h2></div></template><script>exportdefault{name:'watchDemo',data(){return{userName:"abc",age:23}},methods:{change(){}},watch:{//监听userName的变化//有两个参数,newValue表示变化后的值,oldValue表示变化前的值userName:function(newValue,oldValue){console.log('修改前的值:'+oldValue);console.log('修改后的值:'+newValue);},//监听age的变化age:function(newValue,oldValue){console.log('修改前的值:'+oldValue);console.log('修改后的值:'+newValue);}}}</script>界面效果:
2、监听属性和计算属性的区别
监听属性和计算属性的区别主要有下面几点:
计算属性性能更优。一个监听属性只能监听一个属性的变化,如果要同时监听多个,就要写多个监听属性,而计算属性可以同时监听多个数据的变化。监听属性可以获取改变之前的属性值。计算属性能做的,watch都能做,反之则不行。能用计算属性尽量用计算属性。
需求:userName或age改变的时候打印出当前的userName和age值。
用监听属性实现:
<template><div><h2>监听属性</h2>姓名:<inputtype="text"v-model="userName"/><h2>{{userName}}</h2>年龄:<inputtype="text"v-model="age"/><h2>{{age}}</h2><!--打印userName和age的值--><h2>{{info}}</h2></div></template><script>exportdefault{name:'watchDemo',data(){return{userName:"abc",age:23,info:''}},methods:{change(){}},watch:{//监听userName的变化//有两个参数,newValue表示变化后的值,oldValue表示变化前的值userName:function(newValue,oldValue){//console.log('修改前的值:'+oldValue);//console.log('修改后的值:'+newValue);this.info='我的姓名:'+this.userName+',年龄:'+this.age;},//监听age的变化age:function(newValue,oldValue){//console.log('修改前的值:'+oldValue);//console.log('修改后的值:'+newValue);this.info='我的姓名:'+this.userName+',年龄:'+this.age;}}}</script>如果要实现上述的需求,则需要对userName和age都进行监听,监听属性里面的代码都是重复的,如果有多个,那么就要写多个监听属性。在看计算属性:
<template><div><h2>监听属性</h2>姓名:<inputtype="text"v-model="userName"/><h2>{{userName}}</h2>年龄:<inputtype="text"v-model="age"/><h2>{{age}}</h2><!--打印userName和age的值--><!--<h2>{{info}}</h2>--><!--使用计算属性--><h2>{{getUserInfo}}</h2></div></template><script>exportdefault{name:'watchDemo',data(){return{userName:"abc",age:23,info:''}},methods:{change(){}},//watch:{////监听userName的变化////有两个参数,newValue表示变化后的值,oldValue表示变化前的值//userName:function(newValue,oldValue){////console.log('修改前的值:'+oldValue);////console.log('修改后的值:'+newValue);//this.info='我的姓名:'+this.userName+',年龄:'+this.age;//},////监听age的变化//age:function(newValue,oldValue){////console.log('修改前的值:'+oldValue);////console.log('修改后的值:'+newValue);//this.info='我的姓名:'+this.userName+',年龄:'+this.age;//}//}computed:{getUserInfo(){return'我的姓名:'+this.userName+',年龄:'+this.age;}}}</script>如果使用计算属性则只需要写一次就可以实现上面的需求了。
3、监听复杂对象
上面的例子中是监听的普通属性,那么如何监听对象里面的属性呢?看下面的代码:
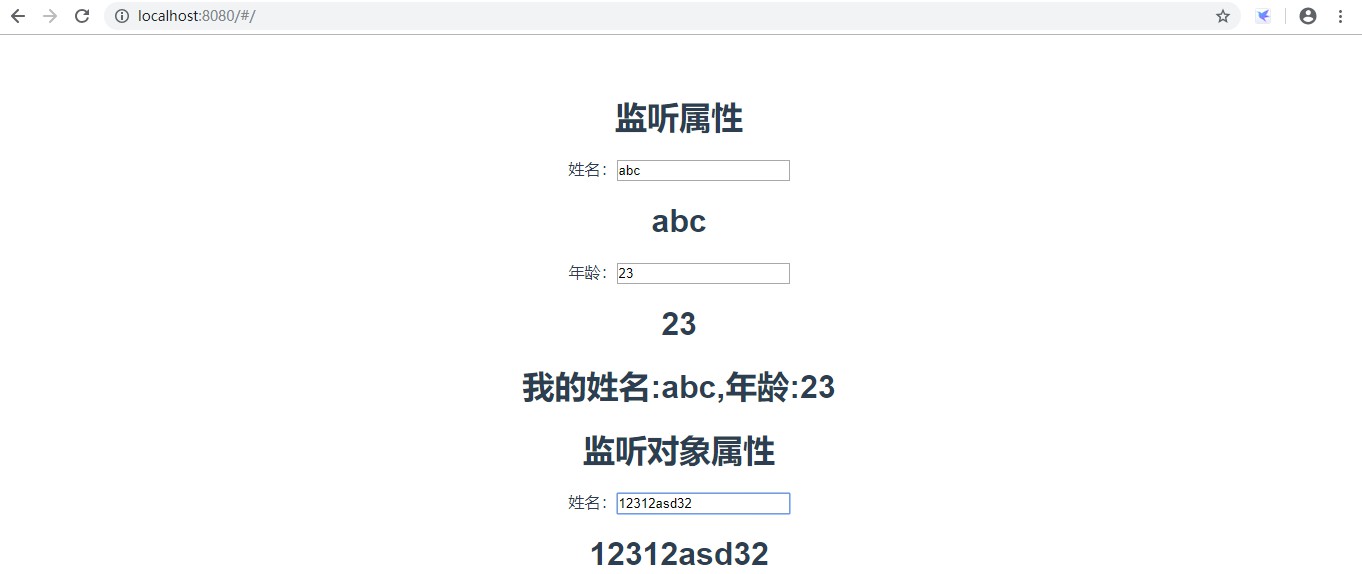
<template><div><h2>监听属性</h2>姓名:<inputtype="text"v-model="userName"/><h2>{{userName}}</h2>年龄:<inputtype="text"v-model="age"/><h2>{{age}}</h2><!--打印userName和age的值--><!--<h2>{{info}}</h2>--><!--使用计算属性--><h2>{{getUserInfo}}</h2><!--监听对象属性--><h2>监听对象属性</h2>姓名:<inputtype="text"v-model="obj.name"/><h2>{{obj.name}}</h2></div></template><script>exportdefault{name:'watchDemo',data(){return{userName:"abc",age:23,info:'',//对象obj:{name:'123'}}},methods:{change(){}},watch:{//监听userName的变化//有两个参数,newValue表示变化后的值,oldValue表示变化前的值userName:function(newValue,oldValue){//console.log('修改前的值:'+oldValue);//console.log('修改后的值:'+newValue);this.info='我的姓名:'+this.userName+',年龄:'+this.age;},//监听age的变化age:function(newValue,oldValue){//console.log('修改前的值:'+oldValue);//console.log('修改后的值:'+newValue);this.info='我的姓名:'+this.userName+',年龄:'+this.age;},//监听对象中属性的变化'obj.name':function(newValue,oldValue){console.log('修改前的值:'+oldValue);console.log('修改后的值:'+newValue);}},computed:{getUserInfo(){return'我的姓名:'+this.userName+',年龄:'+this.age;}}}</script>效果:
能不能执行监听对象呢?答案是可以的,看下面代码:
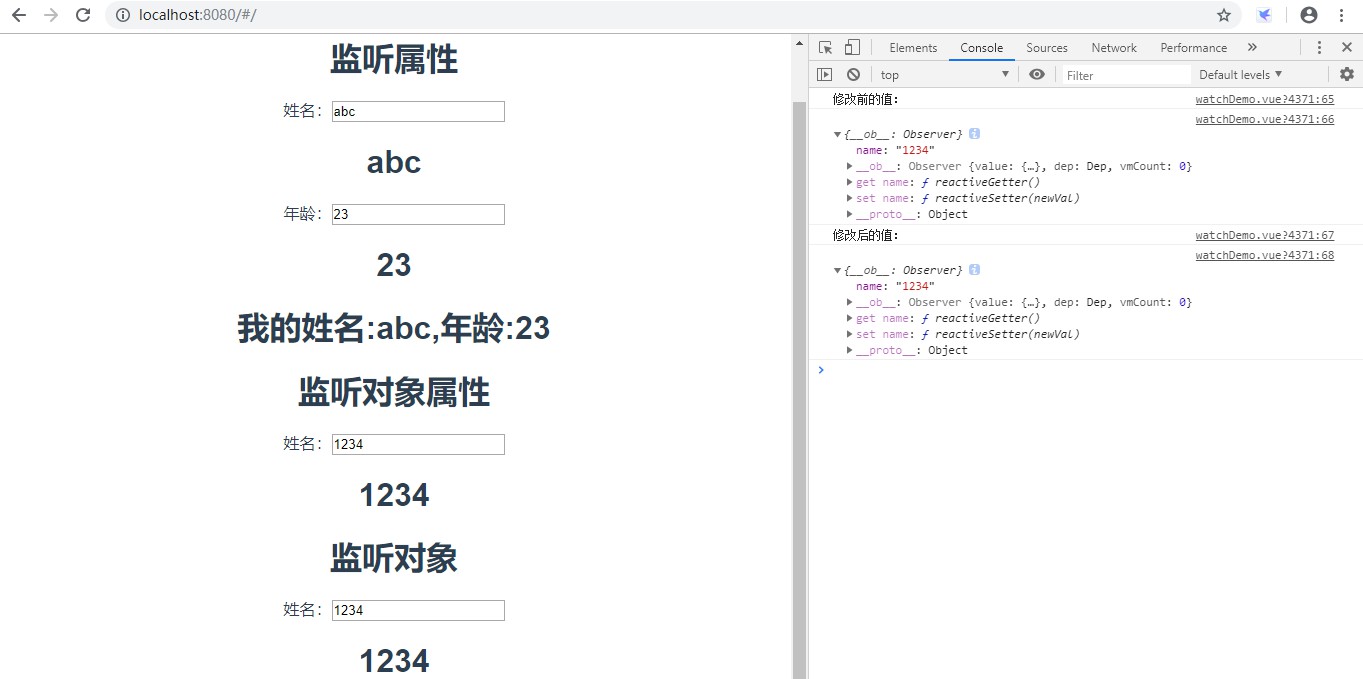
<template><div><h2>监听属性</h2>姓名:<inputtype="text"v-model="userName"/><h2>{{userName}}</h2>年龄:<inputtype="text"v-model="age"/><h2>{{age}}</h2><!--打印userName和age的值--><!--<h2>{{info}}</h2>--><!--使用计算属性--><h2>{{getUserInfo}}</h2><!--监听对象属性--><h2>监听对象属性</h2>姓名:<inputtype="text"v-model="obj.name"/><h2>{{obj.name}}</h2><!--监听对象--><h2>监听对象</h2>姓名:<inputtype="text"v-model="obj.name"/><h2>{{obj.name}}</h2></div></template><script>exportdefault{name:'watchDemo',data(){return{userName:"abc",age:23,info:'',//对象obj:{name:'123'}}},methods:{change(){}},watch:{//监听userName的变化//有两个参数,newValue表示变化后的值,oldValue表示变化前的值userName:function(newValue,oldValue){//console.log('修改前的值:'+oldValue);//console.log('修改后的值:'+newValue);this.info='我的姓名:'+this.userName+',年龄:'+this.age;},//监听age的变化age:function(newValue,oldValue){//console.log('修改前的值:'+oldValue);//console.log('修改后的值:'+newValue);this.info='我的姓名:'+this.userName+',年龄:'+this.age;},//监听对象中属性的变化//'obj.name':function(newValue,oldValue){//console.log('修改前的值:'+oldValue);//console.log('修改后的值:'+newValue);//}//直接监听对象obj:{//handler表示默认执行的函数handler(newValue,oldValue){console.log('修改前的值:')console.log(oldValue);console.log('修改后的值:');console.log(newValue);},//表示深度监听//true:表示handler函数会执行//false:表示handler函数不会执行deep:true}},computed:{getUserInfo(){return'我的姓名:'+this.userName+',年龄:'+this.age;}}}</script>效果:
</div> <div class="zixun-tj-product adv-bottom"></div> </div> </div> <div class="prve-next-news">Vue中的计算属性与监听属性怎么用的详细内容,希望对您有所帮助,信息来源于网络。