Java中二叉树的基础概念是什么
导读:本文共4715字符,通常情况下阅读需要16分钟。同时您也可以点击右侧朗读,来听本文内容。按键盘←(左) →(右) 方向键可以翻页。
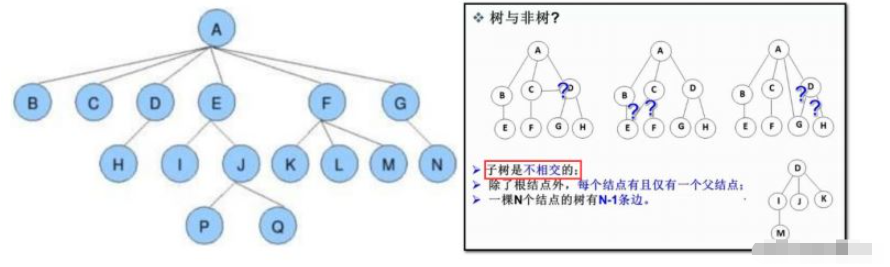
摘要: 1. 树型结构1.1概念树是一种 非线性 的数据结构,它是由 n ( n>=0 )个有限结点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。 把它叫做树是因为它看 起来像一棵倒挂的树,也就是说它是根朝上,而叶朝下的 。1.2 概念(重要)a.节点的度:该节点子树的个数;如上图:A的度为6,J的度为2b.树的度:该树中,最大结点的度就是该数的度;如上图:树的度为6c.叶子节点(... ...
目录
(为您整理了一些要点),点击可以直达。1. 树型结构
1.1概念
树是一种 非线性 的数据结构,它是由 n ( n>=0 )个有限结点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。 把它叫做树是因为它看 起来像一棵倒挂的树,也就是说它是根朝上,而叶朝下的 。
1.2 概念(重要)
a.节点的度:该节点子树的个数;如上图:A的度为6,J的度为2
b.树的度:该树中,最大结点的度就是该数的度;如上图:树的度为6
c.叶子节点(终端节点):度为0的节点(没有子树的节点)
d.双亲结点/父节点:如上图:D是H的父节点
孩子节点/子节点:如上图:H是D的子节点
e.根节点:没有双亲的节点;如上图:A
f.节点的层次:从根开始定义起,根为第1层,根的子节点为第2层,以此类推;
g.树的高度或深度:树中节点的最大层次; 如上图:树的高度为4
2. 二叉树(重点)
2.1 概念
每个节点最多只有两颗子树,度<=2.
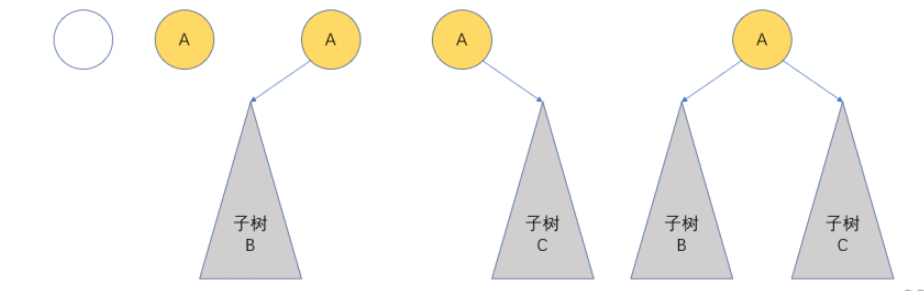
2.2 二叉树的基本形态
2.3 两种特殊的二叉树
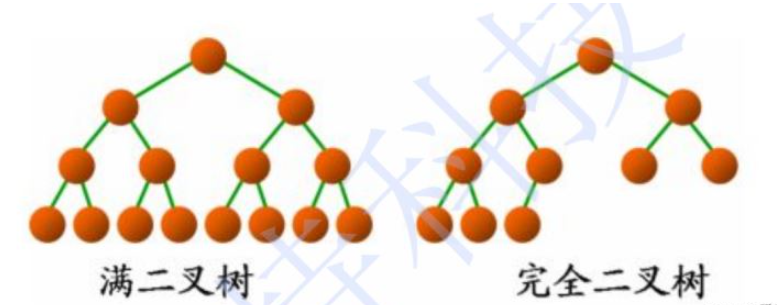
a.满二叉树:非子叶度都为2
b.完全二叉树:满二叉树缺了“右下角”
2.4 二叉树的性质
a.满二叉树
1.高度为K,则有2^k-1个节点
2.层次为K,则该层有2^(k-1)个节点
3.边个数 = 节点个数 - 1
4.度为0有n0个,度为2有n2个,则 n0 = n2 + 1
b.完全二叉树
1.有右孩子必有左孩子
2.只可能有一个度为1的节点
2.5 二叉树的存储
二叉树的存储结构分为:顺序存储和类似于链表的链式存储。
顺序存储:只能存完全二叉树
链式存储:普通二叉树
本次展示链式存储
二叉树的链式存储是通过一个一个的节点引用起来的,常见的表示方式有二叉和三叉表示方式 ,
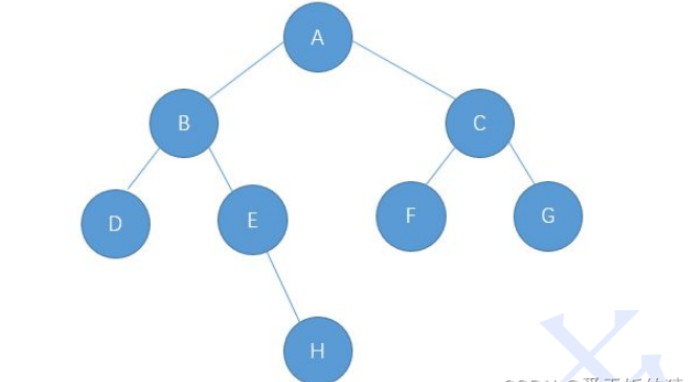
以此图为例, 具体如下:
//孩子表示法privatestaticclassTreeNode{charval;TreeNodeleft;TreeNoderight;publicTreeNode(charval){this.val=val;}}初始化:
publicstaticTreeNodebuild(){TreeNodenodeA=newTreeNode('A');TreeNodenodeB=newTreeNode('B');TreeNodenodeC=newTreeNode('C');TreeNodenodeD=newTreeNode('D');TreeNodenodeE=newTreeNode('E');TreeNodenodeF=newTreeNode('F');TreeNodenodeG=newTreeNode('G');TreeNodenodeH=newTreeNode('H');nodeA.left=nodeB;nodeA.right=nodeC;nodeB.left=nodeD;nodeB.right=nodeE;nodeE.right=nodeH;nodeC.left=nodeF;nodeC.right=nodeG;returnnodeA;}2.6 二叉树的基本操作
2.6.1 二叉树的遍历 (递归)
1. NLR :前序遍历 (Preorder Traversal 亦称先序遍历 )—— 访问根结点 ---> 根的左子树 ---> 根的右子树。
//先序遍历:根左右publicstaticvoidpreOrder(TreeNoderoot){if(root==null){return;}System.out.print(root.val+"");preOrder(root.left);preOrder(root.right);}2. LNR :中序遍历 (Inorder Traversal)—— 根的左子树 ---> 根节点 ---> 根的右子树。
//中序遍历publicstaticvoidinOrder(TreeNoderoot){if(root==null){return;}preOrder(root.left);System.out.print(root.val+"");preOrder(root.right);}3. LRN :后序遍历 (Postorder Traversal)—— 根的左子树 ---> 根的右子树 ---> 根节点。
//后序遍历publicstaticvoidpostOrder(TreeNoderoot){if(root==null){return;}preOrder(root.left);preOrder(root.right);System.out.print(root.val+"");}2.6.2 二叉树的遍历 (迭代)
1.前序遍历
//方法2(迭代)//先序遍历(迭代)publicstaticvoidpreOrderNonRecursion(TreeNoderoot){if(root==null){return;}Deque<TreeNode>stack=newLinkedList<>();stack.push(root);while(!stack.isEmpty()){TreeNodecur=stack.pop();System.out.print(cur.val+"");if(cur.right!=null){stack.push(cur.right);}if(cur.left!=null){stack.push(cur.left);}}}2.中序遍历
//方法2(迭代)//中序遍历(迭代)publicstaticvoidinorderTraversalNonRecursion(TreeNoderoot){if(root==null){return;}Deque<TreeNode>stack=newLinkedList<>();//当前走到的节点TreeNodecur=root;while(!stack.isEmpty()||cur!=null){//不管三七二十一,先一路向左走到根儿~while(cur!=null){stack.push(cur);cur=cur.left;}//此时cur为空,说明走到了null,此时栈顶就存放了左树为空的节点cur=stack.pop();System.out.print(cur.val+"");//继续访问右子树cur=cur.right;}}3.后序遍历
//方法2(迭代)//后序遍历(迭代)publicstaticvoidpostOrderNonRecursion(TreeNoderoot){if(root==null){return;}Deque<TreeNode>stack=newLinkedList<>();TreeNodecur=root;TreeNodeprev=null;while(!stack.isEmpty()||cur!=null){while(cur!=null){stack.push(cur);cur=cur.left;}cur=stack.pop();if(cur.right==null||prev==cur.right){System.out.print(cur.val+"");prev=cur;cur=null;}else{stack.push(cur);cur=cur.right;}}}2.6.3 二叉树的基本操作
1.求结点个数(递归&迭代)
//方法1(递归)//传入一颗二叉树的根节点,就能统计出当前二叉树中一共有多少个节点,返回节点数//此时的访问就不再是输出节点值,而是计数器+1操作publicstaticintgetNodes(TreeNoderoot){if(root==null){return0;}return1+getNodes(root.left)+getNodes(root.right);}//方法2(迭代)//使用层序遍历来统计当前树中的节点个数publicstaticintgetNodesNoRecursion(TreeNoderoot){if(root==null){return0;}intsize=0;Deque<TreeNode>queue=newLinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while(!queue.isEmpty()){TreeNodecur=queue.poll();size++;if(cur.left!=null){queue.offer(cur.left);}if(cur.right!=null){queue.offer(cur.right);}}returnsize;}2.求叶子结点个数(递归&迭代)
//方法1(递归)//传入一颗二叉树的根节点,就能统计出当前二叉树的叶子结点个数publicstaticintgetLeafNodes(TreeNoderoot){if(root==null){return0;}if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){return1;}returngetLeafNodes(root.left)+getLeafNodes(root.right);}//方法2(迭代)//使用层序遍历来统计叶子结点的个数publicstaticintgetLeafNodesNoRecursion(TreeNoderoot){if(root==null){return0;}intsize=0;Deque<TreeNode>queue=newLinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while(!queue.isEmpty()){TreeNodecur=queue.poll();if(cur.left==null&&cur.right==null){size++;}if(cur.left!=null){queue.offer(cur.left);}if(cur.right!=null){queue.offer(cur.right);}}returnsize;}3.求第 k 层结点个数
//求出以root为根节点的二叉树第k层的节点个数publicstaticintgetKLevelNodes(TreeNoderoot,intk){if(root==null||k<=0){return0;}if(k==1){return1;}returngetKLevelNodes(root.left,k-1)+getKLevelNodes(root.right,k-1);}4.求树的高度
//传入一个以root为根节点的二叉树,就能求出该树的高度publicstaticintheight(TreeNoderoot){if(root==null){return0;}return1+Math.max(height(root.left),height(root.right));}5.判断二叉树数中是否存在值为value的节点
//判断当前以root为根节点的二叉树中是否包含指定元素val,//若存在返回true,不存在返回falsepublicstaticbooleancontains(TreeNoderoot,charvalue){if(root==null){returnfalse;}if(root.val==value){returntrue;}returncontains(root.left,value)||contains(root.right,value);}2.7 二叉树的层序遍历
//层序遍历publicstaticvoidlevelOrder(TreeNoderoot){if(root==null){return;}//借助队列来实现遍历过程Deque<TreeNode>queue=newLinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while(!queue.isEmpty()){intsize=queue.size();for(inti=0;i<size;i++){TreeNodecur=queue.poll();System.out.print(cur.val+"");if(cur.left!=null){queue.offer(cur.left);}if(cur.right!=null){queue.offer(cur.right);}}}} </div> <div class="zixun-tj-product adv-bottom"></div> </div> </div> <div class="prve-next-news">Java中二叉树的基础概念是什么的详细内容,希望对您有所帮助,信息来源于网络。